
It probably sounded cool to Lucas at the time, and Solo used parsecs as a measure of time instead of distance – which we already know is wrong.ġ5 Best Star Wars Planets Ranked by Importance One boasting about his piloting skills, as well as the Millenium Falcon’s speed to Luke Skywalker, Han Solo states it can make the Kessel Run in less than 12 parsecs. Perhaps George Lucas thought nobody would notice, but it took one watch of the 1977 film for the designated Star Wars nerds to realize the mistake. The Han Solo quote from A New Hope became iconic for all the wrong reasons. What Does Making The Kessel Run In 12 Parsecs Mean? It can take anywhere between ten seconds and ten hours to cover a parsec in Star Wars. In the end, it’s all about how fast the ship is and how fast you’re driving it. In the Attack of the Clones, the trip from Tatooine to Geonosis lasts for a few hours, despite the distance being less than a parsec. For instance, in The Courtship of Princess Leia, a trip that is 70 parsecs long lasts for more than a week. That’s why sometimes the travels take longer.

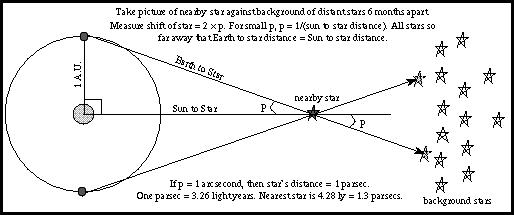
Then you have Class 4, Class 8, Class 16, etc., always covering half the distance. Class 2 hyperdrive ships, such as the Star Destroyers, travel half of that in a day (roughly 6 750 light-years). A regular X-Wing has a class 1 hyperdrive, meaning it covers 12500 light-years in a day. We know the Millenium Falcon is a beast, though. We know that a parsec is 3.26 light-years, meaning Han Solo can cover one parsec at just under 11 seconds – that is, if he maintains top speed. So, Han Solo’s Millenium Falcon has a class 0.5 hyperdrive and is said to be able to travel 25000 light-years in a day, or a bit over 1000 light-years an hour. Star Wars Chronological Timeline With Infographic It depends on the ship, of course, but we can find a general point. Let’s do some math using the information we have to see how long it takes to travel a parsec in Star Wars. I won’t get into details about how hyperspace works, but generally, it allows them to travel a whole lot faster than the speed of light. That’s because they use something called the hyperspace. The fastest ones even measure it in seconds. However, in Star Wars, spaceships can cross a parsec in minutes. If you traveled at light speed, it would take you 3.26 years to cross a parsec. That is our fastest outward-bound spacecraft ever. That means it would take roughly around 18000 years to travel a light-year.Ī parsec is 3.26 light-years, meaning it would take the Voyager 1 between 5800 years to cross the distance of a parsec. To this day, it has traveled roughly around 0.0025 light-years from Earth. So, the Voyager 1 has been out in space since 1977. It can measure, to within 20 percent accuracy, the distances of stars that lie tens of thousands of light-years away.Before we get into the time needed for Star Wars starships to travel the distance of a parsec, I want to put into perspective what a huge distance that is for our standards. The European Space Agency’s Gaia mission, currently underway, can measure parallax angles of just a few millionths of an arcsecond. That’s why a parsec has that value, and not any other.Īlthough astronomers often measure distant objects in parsecs or megaparsecs (1 megaparsec is 1 million parsecs), only nearby objects have parallaxes, or shifts on the sky, that we can actually measure. And a parsec is the distance - 3.26 light-years - that a star must lie from the Sun for its parallax angle to be exactly 1". The two different sightlines, one at each end of Earth’s orbit, create a triangle the parallax angle is defined as half the angle at the triangle’s apex. If you draw a simple diagram, you’ll see that the distance the star appears to move is related to the angle at which it is viewed. Translated to the stars in the sky, two photographs of the same nearby star taken six months apart will show it appearing to move against the background of more distant stars because Earth has moved to the other side of the Sun in its orbit. Your finger will appear to shift because each eye views it from a slightly different angle. Close just your left eye and observe where your finger appears against the background next, open your left eye and close your right. One of the simplest ways to see for yourself how this works is to hold your hand at arm’s length in front of your face and raise one finger. Over the course of several months, nearby stars appear to move with respect to more distant objects - an effect called parallax - because as our planet moves, our viewpoint changes. Earth circles the Sun, making one complete orbit per year.
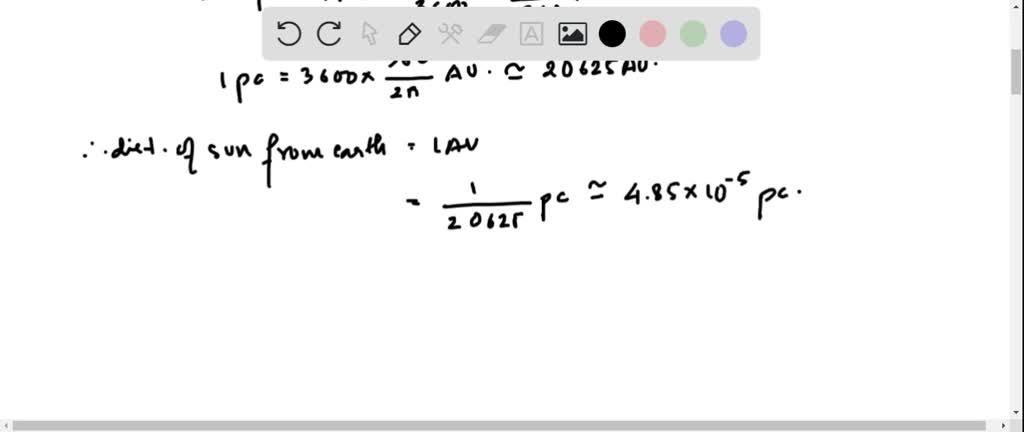
Q: Why is a parsec 3.26 light-years and not some other number?Ī: A parsec, or “parallax second,” is defined as 3.26 light-years because of how it is measured.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
